AvaCloud VRF Quickstart Guide
Congratulations! You have just completed the AvaCloud VRF onboarding flow. This quickstart guide assumes you have completed the VRF setup process successfully on your L1 and have access to an active VRF Proxy dashboard.
AvaCloud VRF is a service that provides on-chain random values to Avalanche L1s deployed via AvaCloud. This service leverages Chainlink VRF on the Avalanche C-Chain to fetch the random values and pass back to the L1. For more details on the design and architecture, please see the contracts.
Prerequisite
This guide uses Foundry for smart contract development. If you do not have Foundry, run the following command:
To ensure proper installation, run:
Integration Steps
Once the VRF Proxy is deployed, the steps to integrate with a solidity smart contract are simple.
- Create a new forge project. This will create a new repository. After running, you should see the following files in the directory.
- Install dependencies.
Add the following to your foundry.toml file under the [profile.default] header
- Create a new smart contract file in
/srcand import the required dependencies. Create a default constructor to accept thevrfProxyAddressfound in the AvaCloud portal.
- Implement contract. By inheriting
VRFConsumerBaseV2, you must implementfulfillRandomWords()as a callback once a VRF request is returned. Our implementation allows users to guess a random number between 1 - 10, and rewards them if they guess correctly.
- Deploy contract: take note of the contract address
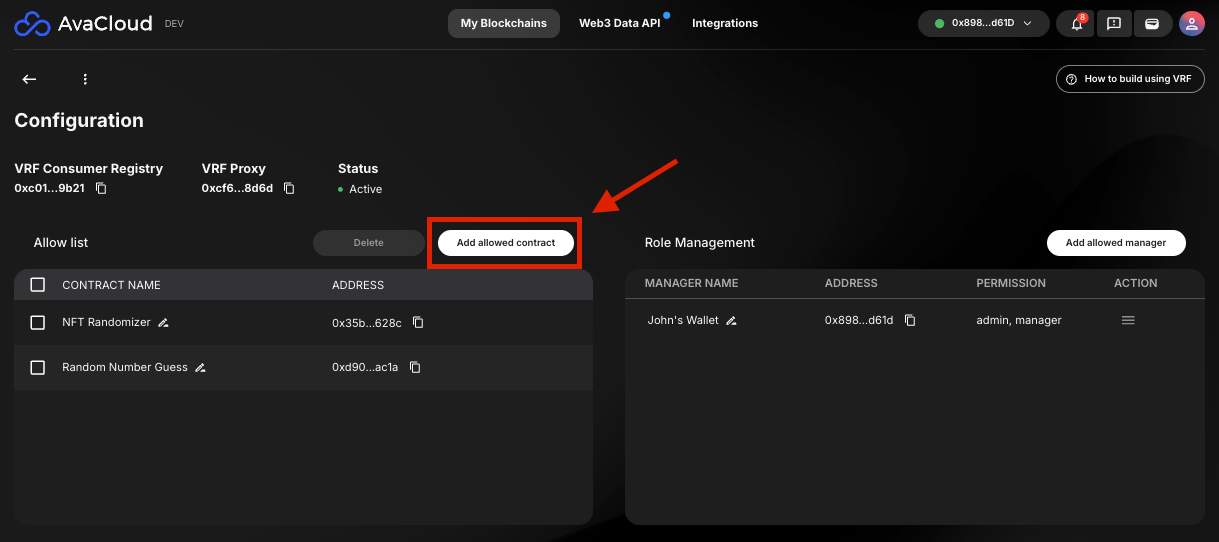
- Add the contract address to the Consumer Allowlist in the AvaCloud Portal VRF module
- Test the contract. The last value is the guess, for this demo we are guessing 5.
To get the requestID, look in the event logs for your smart contract address
(ours is 0xc615f4614056bc15744db453d119134ee48e1cde). Since the last value in the topics list is 0x0...02,
the requestID is 2
Then, query the guesses mapping to see if your request was successfully resolved.
Since the last value is true, we know our request was resolved. Finally, we can check to see what random valued was returned and if we guessed correctly.
Unfortunately, we did not guess correctly, but we now know our contract successfully returns a random value from C-Chain!
Congratulations, we have now successfully created and deployed a contract to use random values! Now you can extend this functionality in your own smart contracts.
Full Contract Implementation
If you need more help, explore our other articles or reach out to our support team via chat or email [email protected]. All examples provided are for demonstration purposes only.
Learn More About AvaCloud | Download Case Studies | Schedule an AvaCloud Demo